

Blockchain has been a reliable technology for over a decade and has been applied in many specialized disciplines. Although the concept of a chain of cryptographically secure blocks was first proposed at the start of the 1990s, blockchain technology only became widely known after the launch of Bitcoin in 2008. In contrast, Hedera Hashgraph was first introduced in 2017, nine years after Blockchain entered the tech industry. Despite this time difference, it would be unfair to conclude that one technology is more developed than another, given how swiftly and effectively technology may now advance. It only matters how much effort is constantly invested in the development. So, will Hashgraph replace Blockchains? Let’s delve deeper to find it with a detailed comparison of Hashgraph vs. Blockchain.
Blockchain is the most widely used type of distributed ledger technology. The technology operates like this: there are nodes with a copy of the Blockchain that verifies and carries out transactions. All essential information is recorded in a block after a transaction has been completed, and that block is then chronologically tied with the one preceding it. As a result, a network of blocks is created that cannot be altered or removed. The video below explains the core concepts of blockchain and how it can help businesses to be more efficient.
Many people still identify Blockchain with cryptocurrencies because it was first developed as a technology to support Bitcoin, although this is no longer the case. Numerous industries, including logistics and supply chain management, healthcare, fintech, real estate, gambling, eCommerce, eGovernance, and others, have already felt the impact of blockchain technology. To learn more about blockchain, you may refer to this article: What is blockchain technology?
Reach out to us today for a no-obligation consultation
Leemon Baird, founder and chief scientist of Hedera Hashgraph, developed it as a distributed ledger solution. Hedera is a patented, privately owned technology, and Swirlds Corporation is the owner of the intellectual property rights to it. The key merit of Hashgraph is that it achieves consensus without the dependency on validator nodes in the network or the presence of malicious nodes.
This technology represents a distinct approach. Instead of blocks, it features a graph structure. When nodes exchange information, a graph of connections is created, and Hashgraph stores data as events rather than a series of interconnected blocks.
Hedera is frequently referred to be the next-generation Blockchain by tech experts, even though it has yet to gain much more traction as Blockchain. We must delve a little deeper into determining whether Hedera can outperform Blockchain. Learn more about Hedera Hashgraph in detail
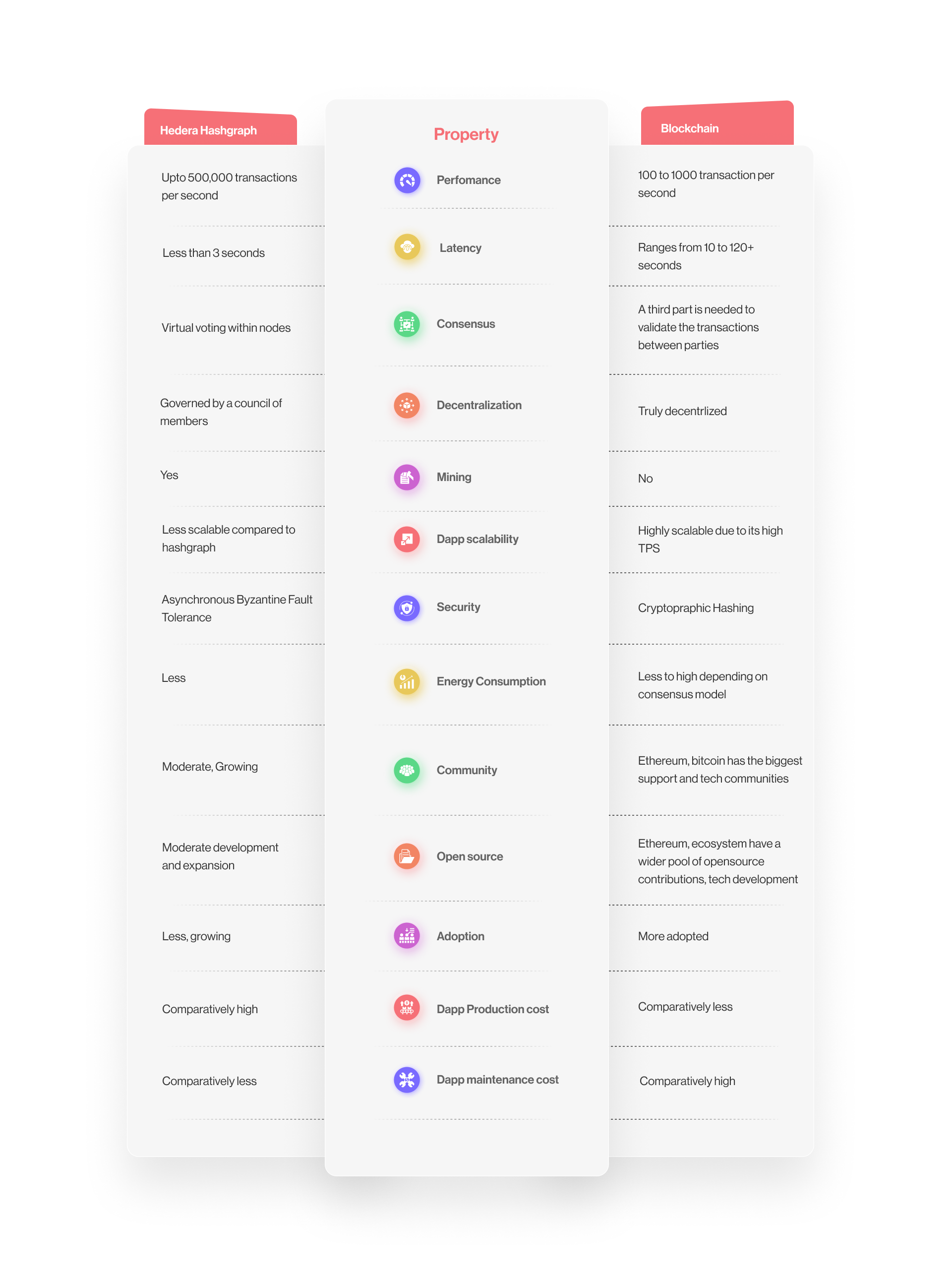
Let’s analyze the merits and demerits of Blockchain and Hashgraph with respect to factors that determine the success of a DLT in the market. Thus we can know whether Hashgraph will Replace Blockchains.
The strength of the developer community and the ease of dApp development are key factors that determine the success of a DLT in the market. When we analyze, Hedera does not fall behind in ease of dApp development. Because Hedera supports Solidity, the same programming language used by developers to develop dApps in Ethereum. A developer who can launch a smart contract on Ethereum can easily launch it on Hedera. However, regarding the developer community’s strength, Hedera is not as powerful as compared to Ethereum. Ethereum being older and the first blockchain to introduce the concept of smart contracts, had an early mover advantage in building a strong developer community distributed worldwide. One merit of hedera is that, since it supports Solidity, the developer community of Hedera can directly benefit from the developer community of Ethereum.
Solidity is popular among blockchain programmers. The Ethereum team created this programming language to create Ethereum smart contracts. It is important to remember that Solidity has a learning curve and is one of the most popular languages in the blockchain community. Likewise, on Ethereum, Vyper can be used to create smart contracts. Cadence is another programming language. It was developed specifically for the Flow blockchain Programmers can also write code in languages like Java, JavaScript, Python, C++, C#, Go, and Rust.
The languages most frequently used with Hedera Hashgraph are Java, JavaScript, and Go, and they now support Solidity as well. Although there are more languages on this list, finding programmers for Hashgraph-based applications will be easy because a huge developer community is quite familiar with them. In addition, developers can use Solidity and Vyper to write smart contracts for Hedera. So, developer community strength in the context of Hashgraph vs. Blockchain doesn’t seem like a strong factor that enables Hashgraph to replace Blockchains.
Any distributed ledger technology should have a consensus algorithm for achieving the necessary agreement between the nodes about the entire system’s state. In addition, consensus directly impacts network security and transaction performance. The Proof of Work (PoW) consensus protocol is used by the two most widely used blockchains, Ethereum and Bitcoin.
Nodes, in this instance, are miners who must complete challenging mathematical problems to add a new block of data to the Blockchain. The first one who finishes will earn some cryptocurrency. The Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus is used by several extensively used blockchains, including Flow, Cardano, Polygon, Tezos, and Avalanche. This algorithm is the best substitute for PoW. Here mining is not required, and nodes must stake their coins to participate in the network.
Contact us today for a no-obligation consultation
Additionally, there is the Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) protocol, a more sophisticated variation of PoS. This algorithm builds well-known blockchains like Tron, WAX, EOS, and Steem. Other blockchain consensus techniques include Proof of History (PoH), Proof of Authority (PoA), and Proof of Elapsed Time(PoET). These are less well-known but still functional.
In a very similar manner, the Hashgraph consensus operates like this. When a node communicates with another node, it relays all the details of that communication to an additional, random node. The next random node must receive this information from that other node, so the entire network is kept informed on what’s happening.
Technically, nodes are components that share data on the hash graph. They reach a consensus through electronic voting and keep information like timestamps, hashes, and event transactions. High transaction speeds of up to 10,000 transactions per second can be achieved with the help of this consensus-building strategy.
Hashgraph is significantly quicker than the most popular blockchains. Hedera is also more energy-efficient than Ethereum and Bitcoin because it doesn’t need a lot of processing power because of the Hashgraph consensus. Considering the superior performance, Hashgraph can Replace Blockchains in the future.
Both Hashgraph vs. Blockchain could be an option for launching smart contracts. In fact, without them, transactions are not feasible. The most notable feature of Blockchain smart contracts is that they are immutable. You must specify in advance what conditions the smart contract will execute transactions. Developers will incorporate these requirements into the code, and smart contracts will then execute transactions when the requirements are satisfied.
The data becomes immutable and cannot be modified or removed once the transaction is finished and recorded on the Blockchain. Once developers deploy them, it is impossible to change the code. This feature is very relevant in sectors like finance and supply chain management. However, it can create difficulties for developers as they need to write code consciously, as one error will cost them money and time they put into it.
Hedera smart contracts are immutable but still have the option to upgrade them. This feature is implemented to allow developers to fix bugs, introduce updates and resolve disputes. Hedera smart contracts are processed in the order in which they were received. On the Blockchain, the processing is frequently based on how much gas you are willing to pay (the transaction fee on Ethereum) or whether the miner chose your transaction first. Hedera offers lesser transaction fees compared to most blockchains.
The bitcoin blockchain is considered the one truly decentralized Blockchain. Ethereum comes right after bitcoin in terms of decentralization. According to the Morgan Stanley Wealth Management report, the top 100 addresses hold about 39% of ETH, Ethereum’s cryptocurrency, compared to 14% for Bitcoin in terms of concentration risk. So ether is held by a relatively small proportion of accounts.
One of Ethereum’s co-founders, Vitalik Buterin, coined the phrase “Blockchain Trilemma.” The dilemma is that developers are challenged to develop scalable, secure, and decentralized blockchains without these requirements being overlooked. This explains why blockchains frequently exhibit great levels of scalability and security but lack decentralization. Or, like Ethereum, they are secure and decentralized but need help with scaling. The blockchain community still needs to address the trilemma.
Get in touch with us today!
Hedera hashgraph is not truly decentralized. The Hashgraph network is owned by 39 well-known companies, including IBM, Chainlink Labs, Ubisoft, Google, LG, Boeing, and others. They each have an equal 2.6% influence on decision-making as members of the Hedera Global Governing Council.
Decentralized technology would not have a central authority that might have such a significant impact on the network in an ideal world. Hedera claims that steps are already being taken toward decentralization. Hedera is currently a publicly permitted platform with intentions to become publicly permissionless regarding accessibility. In the case of Blockchain, it can be private, public, or even hybrid.
The Blockchain’s structure and powerful cryptographic hashes keep watch on the network’s security. A potential hacker would have to alter not only the block containing a specific piece of data but also every block connected to it, which is an impossible process. Additionally, there is no option to modify the information because recorded data is unchangeable.
On the other hand, the security gold standard for hashgraph technology is the asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance algorithm (aBFT), which makes it impossible to tamper with data even when there are bad actors on the network.
When deciding which technology is better, Hashgraph vs. Blockchain, it depends on the specific application utilized. We cannot conclude that Hashgraph will replace Blockchains. It depends on the individual application utilized to determine if Hashgraph or Blockchain is a better solution. For instance, some applications benefit from higher throughputs and faster transaction speeds, in which case a hashgraph would be preferable.
However, blockchain might be preferable for applications needing a high level of decentralization and security. Ultimately, both technologies are effective resources for distributed applications, and it is up to the developer to select which one is best suited for their needs.
Reach out to us today for a no-obligation consultation