

DeFi or Decentralized Finance is the latest hot trend in the fintech space and has caught the attention of several entrepreneurs, especially those involved in the BFSI sector. On preliminary research, you’ll see that DeFi is the technology used to enable financial services on a decentralized nature. Ruling out the middle men like banks and financial institutions from the equations and leveraging automation to execute direct financial transactions between the participants.
Isn’t this similar to what we all read about blockchain technology’s applications in the financial services industry?
Is DeFi just a new buzz name given to the same old use cases we read a lot? Or Is there something revolutionary and new about DeFi?
Let’s learn more about DeFi from the below sections:
DeFi stands for “decentralized finance” and acts as a financial ecosystem that is built on top of blockchain technology. It is a collective term for services like investing, borrowing, lending, trading, and other financial services based on decentralized, non-custodial infrastructure.
It involves the use of decentralized networks and open source software to develop various financial services and products. The idea is to build and operate financial dApps on top of a transparent and trustless framework, such as permissionless blockchains and other peer-to-peer (P2P) protocols.
Between September 2017 and August 2020, the total value locked up in DeFi contracts has exploded from US$2.1 million to US$6.9 billion (£1.6 million to £5.3 billion). Since the beginning of August alone it has risen by US$2.9 billion.
Decentralized Finance can include digital assets, protocols, smart contracts, and dApps. DeFi products are well received in the market, the image below shows some of the very recent updates in the DeFi space.
DeFi provides a completely decentralized option for a trustless financial system. There are different types of lending and credit platforms within the DeFi space. These projects employ different strategies to allow users to borrow from and lend to each other with no central entity involved.
The main uses for DeFi include:
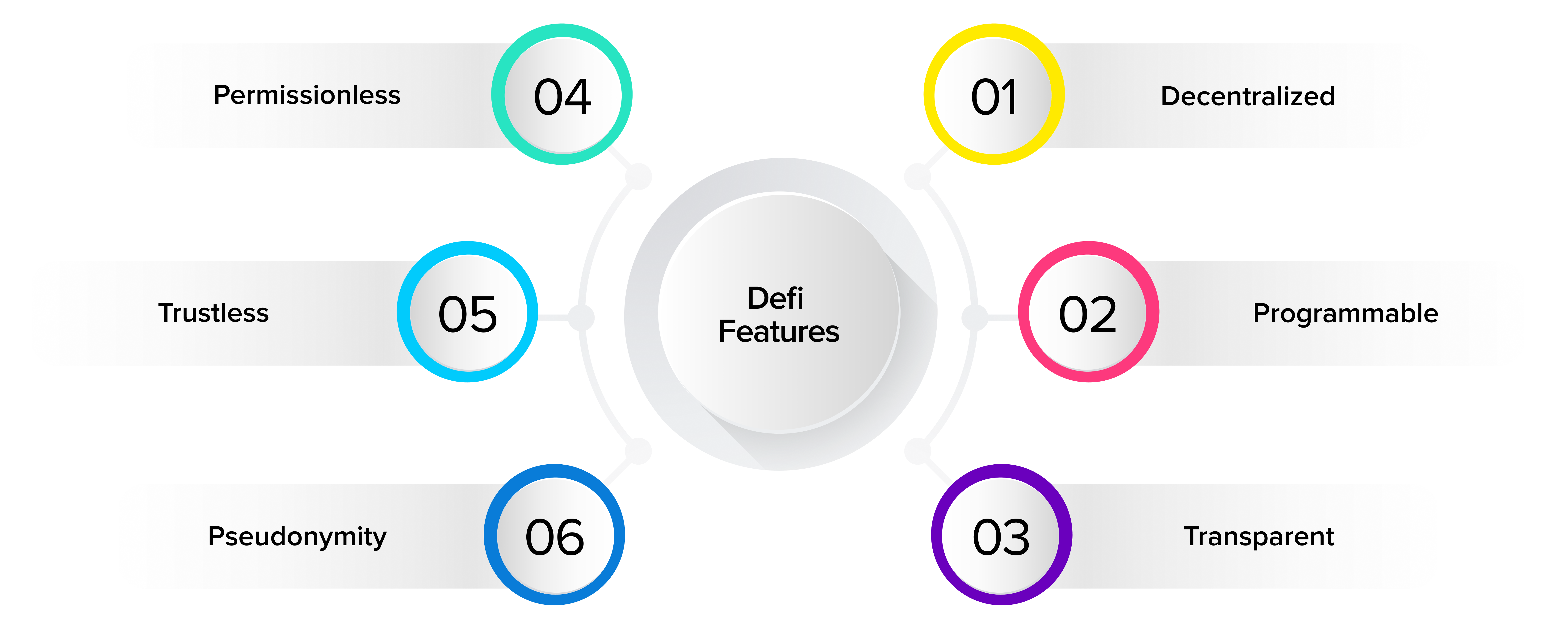
The following are a few basic characteristics of a DeFi app. However, these are not strict defining factors for a DeFi dApp as many of the existing DeFi apps in the market do not all of there characteristics.
Let us have a look at some of the main points of difference that set DeFi dApps apart from traditional banking systems.
Business operations aren’t under the management of an institution and its employees. All the rules are written in code (or smart contracts). Once the smart contract is deployed to the blockchain, DeFi dApps can run themselves with little to no human intervention
DeFi is developed on top of a blockchain. This means that it inherits the security and transparency that comes with blockchain technology.
Its core benefits are-
Reach out to us today and get started!
People have used the barter system for exchanging goods and values since time immemorial. Around 600 B.C., they switched from the barter system to the concept of money. And by the 15th century, banking and financial systems evolved and expanded to a great extent. Over these years, several reforms have been made to banking systems and today we have a fairly good system.
Financial services have typically involved a centralized approach, it has central authorities that are responsible for issuing currency and facilitating trade. These authorities have the ultimate power to manage and regulate the flow and supply of currencies in the market. It’s all good. We are used to it. We’ve been running businesses, managing finances with this age old and proven method. But, the question is, is there room for improvement?
Financial system has undergone major changes from time to time. Are we on the cusp of the next major change in the financial system? Change is inevitable and it happens if a system is not as efficient or not serving the needs of the greater mass. So we need to take a look at the state of the existing systems. Are our current financial systems absolutely fail proof? Let’s consider a few examples.
International payments tend to be a very laborious process. They take a lot of time and can be extremely risky as well. Additionally, the chances of hidden fees cropping up are very high. Businesses can incur flat fees on incoming wire transfers, which can be a $20–50 fee assessed on receiving the wire. On top of this, intermediary banks are sometimes in the middle of a transaction and charge their own additional wiring fee. These banks also charge a premium on foreign exchange, which is often a large margin above the mid-market exchange rate. These types of payments are also very susceptible to fraud. These limitations create several reservations around international payments.
The recession of 2008 encompasses both the U.S. recession, officially lasting from December 2007 to June 2009, and the ensuing global recession in 2009. A great deal of damage was done to financial institutions all over the world due to excessive risk-taking by banks combined with the bursting of the United States housing bubble.
The economic crisis initially started in the U.S. but eventually spread to the rest of the world. This is because U.S. consumption accounted for more than a third of the growth in global consumption between 2000 and 2007 and the rest of the world depended on the U.S. consumer as a source of demand.
According to the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission, the Great Recession was avoidable. Some of the key contributing factors that led to the crisis included the failure of the government to regulate the financial industry, extremely risky decisions taken by financial institutions, weak and fraudulent underwriting practices and overall, a faulty banking model.
The great recession clearly demonstrated the dangers associated with leaving a centralized authority in charge of financial systems. Humans can make mistakes and take unnecessary risks. The decision of a single entity can adversely affect the entire world.
What if central authorities make bad decisions while issuing currency? For example, Venezuela experienced severe currency instability due to the government’s inefficient monetary policies, which included printing huge amounts of money amid an oil price drop. This resulted in severe inflation exceeding 1,000,000% as per IMF data.
Clearly, there is room for improvements for the current financial systems. So, is that why we have blockchain based crypto currencies? – to solve these problems with the financial systems?
Bitcoin, along with other types of cryptocurrency have helped in solving this problem to a certain extent by facilitating secure peer-to-peer trading without the need for intermediaries like a bank for trade settlement. This gives users complete control over their assets. However, this is not a complete solution for the problems we discussed above. Although cryptocurrencies have decentralized currency issuing and storage, it has not decentralized the financial system as a whole. The major issues that stunt the growth of decentralization in the finance industry include-
A centralized system allows risk and vulnerabilities to accumulate in the centre of the system, which consequently endangers the system as a whole. In such a scenario, it is important to make our financial system more fair and transparent. The solution lies with decentralized finance, which can allow us to take control of our assets and our financial decisions.
Reach out to us today and get started!
Let’s take a look at some of the most popular decentralized finance applications on the market
This refers to s a digital money lending platform built on a blockchain. Similar to a bank, users deposit their money and earn interest, if someone else borrows their digital assets. However, smart contracts are used instead of third parties to dictate the loan terms. These contracts are also responsible for connecting lenders and borrowers, and distributing the interest. It offers several advantages over the traditional lending/crediting services –
Examples for such protocols include Dharma and BlockFi. The latter allows users to borrow and lend digital assets but employs familiar credit models like credit checks and a company processing loan requests on the backend.
Unlike other crypto coins which have a volatile value, stablecoins are blockchain-issued tokens designed to hold on to a specific value. A stablecoin can be pegged to a cryptocurrency, fiat money, or to exchange-traded commodities (such as precious metals or industrial metals).
Stablecoins can be primarily categorized into 3 types:
Decentralized exchanges are very different from centralized ones like Coinbase. They involve peer-to-peer transactions of digital assets between two parties on the blockchain with no third-parties involved. The advantage of this approach is that there are no sign-ups, no identity verification, or any withdrawal fees. IDEX is the most popular DEX – a dapp on Ethereum blockchain. Other DEXs include Binance DEX, Radar Relay, and EtherDelta.
Other types of open marketplaces focus on non-fungible tokens (NFTs) exchange. These tokens are often referred to as crypto-collectibles. OpenSea and Rarebits are two such platforms that help the exploration, discovery and buying or selling of such crypto-assets. There are also some marketplaces like District0X which allows for the creation of marketplaces to vote on governance procedures.
DeFi boosts the functionality and reach of money, while providing a financial system that is more open and liberalised than ever before. The DeFi market is quite small in relation to traditional finance, but it is expanding at rapid rates. This creates much hope for a financial revolution that supports decentralization and transparency. It takes us one step closer to democratizing the global economy, making money and payments universally accessible to everyone.
To know how to launch a DeFi project, refer this article – How to launch a DeFi project
Reach out to us today and get started!