

As the world is embracing the big data era, the popularity of edge computing for businesses is once again increasing, due to the growing demands for real-time and local data analytics. Edge computing creates more efficient ways for businesses to optimize operational efficiency and discovering newer opportunities for improving performance and automate core business processes.
Today, the amount of data being generated, transmitted and stored has reached unprecedented levels. These levels continue to increase with the advent of IoT and 5G networks. Not so surprisingly, it has reached a point where the complexity of data that is generated by connected devices has outpaced network and infrastructure capabilities.
Around 10% of enterprise-generated data is created and processed outside a traditional centralized data center or cloud. By 2025, Gartner predicts this figure will reach 75%
This is why several businesses are turning to alternative options for data processing like edge computing. Edge computing and mobile edge computing on 5G networks enable faster and more comprehensive data analysis, creating the opportunity for deeper insights, faster response times and improved customer experiences.
Edge computing refers to computing and data storage that occurs closer to the data source, instead of a central cloud location. This doesn’t make the cloud obsolete, it just brings the cloud closer to you. Basically, edge computing will reduce the number of processes being executed in the cloud by moving these processes to local locations like a user’s computer, an IoT device, or an edge server. This is done to reduce the amount of long-distance communication that occurs between a client and a server.
Let's talk!
For example, think about a business that uses IoT CCTV cameras for surveillance. These cameras transmit a raw video signal and continuously stream that signal to a central cloud server. Once the video transmission reaches the cloud server, it is sent to a face recognition application to ensure that only the clips that feature human faces will be stored in the database of the server. This puts a huge amount of strain on the Internet infrastructure of the business, since a significant bandwidth gets used up by the considerable volume of footage being transferred. Moreover, the cloud server will also experience a very heavy load as it has to process the footage from multiple cameras at the same time.
What if this face recognition application was moved to the edge of the network? This would mean that each camera would use its own internal computer to perform the face recognition process and send the required footage to the cloud server accordingly. By incorporating edge computing into the process, the business can reduce the bandwidth use along with the associated costs since most of the footage will not be transmitted to the cloud server. The cloud server will store only the required footage, which makes it much easier for it to interact with multiple cameras simultaneously. A high level architecture of how edge computing and cloud computing can co-work, is as shown in the diagram below.
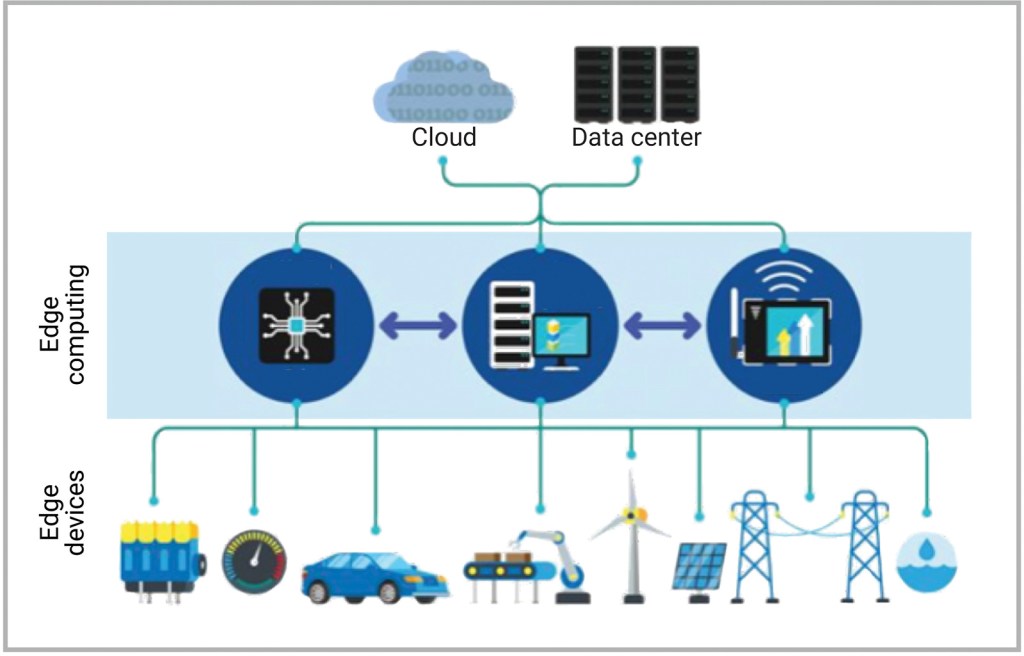
In Edge AI, the AI algorithms are processed locally on a hardware device, without requiring any connection. It uses data that is generated from the device and processes it to give real-time insights in less than a few milliseconds. For example, if your phone has the ability to register and recognize your face to unlock your phone, it will probably use complex algorithms on the edge to process your face data in real-time. This is because there isn’t enough time to send this data to the cloud, process it and wait for the insights. Here is a demo video of an AI-based face-mask detection system that uses edge computing.
Edge computing can complement AI as it helps overcome the technological challenges associated with AI-enabled applications. Businesses should prioritize edge computing in their AI applications since it provides several benefits like-
As per a report by Tractica, AI edge device shipments are expected to increase from 161.4 million units in 2018 to 2.6 billion units by 2025.
Here, the top AI-enabled edge devices include smart speakers, mobile phones, head-mounted displays, PCs/tablets, automotive sensors, robots, drones and security cameras. Wearable health sensors will also see an increased application of AI.
There are many benefits that are associated with the use of edge computing in business. It allows for efficient data processing that is much more secure and reliable when compared to alternate methods.
Several businesses need to ensure that their business processes are being executed at optimal speeds. For example, banks depend on high-frequency trading algorithms, and even a millisecond of delay can result in serious losses. Businesses that offer data-driven services to customers will need to ensure high speeds, since delays can result in a frustrated customer who can damage the reputation of the company.
The use of edge computing can help businesses increase network performance with lower levels of latency. When a device communicates with a distant server, it will cause a delay.
The interaction between any kind of device or application with an external server can experience delays and reduce the overall speed of the associated processes. The duration of these delays will vary based upon their available bandwidth and the location of the server, but these delays can be avoided altogether by bringing more processes to the network edge.
In some cases, edge computing can create problems with network visibility and control, as the edge devices may be located in remote locations. With the advent of IoT technoloy, each IoT device could be a potentially vulnerable endpoint ( if proper security measures are not implemented). But as the number of IoT devices increases, so does the security vulnerabilities. If edge devices are installed without a detailed security testing, loopholes in edge security could provide hackers easy access to the core of a network.
Edge computing can provide some benefits when it comes to the network security. Data transmitted through a network can be hacked and potentially exploited even if it is encrypted. But using edge devices, the total volume of dat transmitted through a network is considerably reduced. Moreover, in most cases of edge computing, the data is distributed across many devices, only storing fractions of data in each device. Even if couple of the edge devices are compromised by hijackers, the potential damage caused to the business is comparatiely low. This can be beneficail for many businesses especially ones in healthcare, automated UAVs.
Let's talk!
Businesses are constantly expanding, and this makes it impossible to predict the requirements for IT infrastructure. Building a dedicated data center can be very costly due to up-front construction costs and ongoing maintenance. Additionally, if the business grows more than expected, it may not have adequate computing capacity. This is why computing technology like the cloud and edge computing is so important for businesses, as they allow for much better scalability.
Nowadays, companies do not need to build a centralized data centre that will put a strain on their resources. Instead, they can use edge computing and expand their edge network reach according to their needs. The flexibility of not having to rely upon a centralized infrastructure allows them to adapt quickly to evolving markets and scale their data and computing needs more efficiently.
Edge computing is much more reliable since the IoT edge computing devices and edge data centers are located closer to the end users. This makes it less likely for a network problem in a distant location to affect local customers. Even during a data center outage, IoT edge computing devices will continue to operate on their own since they process all the data natively. Additionally, the lower levels of latency and enhanced network performance provides a seamless experience that cannot be compared with cloud computing.
By reducing the distance over which data is transported before it is processed, edge computing helps to reduce telecommunications latency and bandwidth costs. Bandwidth and cloud resources are finite and hence, put a strain on financial resources. By incorporating edge computing into their IT infrastructure, companies can save sizable amounts of money and resources.
Edge computing can be applied in a variety of industries for enhanced data processing techniques and security. They include-
Cars, planes, trains and other methods of transportation can greatly benefit from edge computing. It can help in battery monitoring and predictive maintenance by aggregating key data insights and performing a real-time inspection of key battery parameters. For example, the airplane manufacturer Bombardier’s C-Series has been heavily outfitted with sensors to immediately detect engine performance problems. Over 12 hours of flying, the airplane generates 844 TB of data. Edge computing allows real-time processing of the data, so the company can proactively deal with engine issues.
Edge computing is also a key component of self driving vehicles. Autonomous cars require extremely fast processing speeds that cannot be achieved with cloud computing. Processing data on the edge can minimize network overhead, while data that needs further analysis or permanent storage can be sent to the cloud at a later time.
Wearable health-monitoring devices are becoming increasingly popular, from fitness trackers like fitbits to glucose monitors and smartwatches. In order to make these health wearables more effective, real-time data analysis is essential. This is where edge computing comes in. It allows for faster data processing, which provides key health insights immediately. Experts say collecting data from smart wearable devices may prove highly useful in cases of a pandemic, where faster data processing near the source has the potential to be life saving.
Additionally, speedy data processing can be extremely beneficial for remote patient monitoring, inpatient care, and healthcare management for hospitals and clinics. Doctors will be able to provide faster, better care to patients while also adding an additional layer of security to the patient-generated health data (PDHD).
Edge computing can also help use big data, along with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities to predict patterns in the spread of deadly diseases. For example, US-based BlueDot is a geofencing software company that is using data from social media, text messages, and other online communications to predict the spread of the novel coronavirus (Covid-19).
Agricultural farms are often located in remote areas with unfavorable conditions, which lead to major connectivity issues. Currently, smart farms that are looking to solve these issues are investing in expensive fiber, microwave connections, or full-time satellites. Edge computing offers a much more cost-effective alternative.
Smart farms could use sensors to monitor soil conditions, temperature, and weather conditions. Edge computing could then provide farmers with detailed insight quickly as data will be processed locally. It could also help reduce food wastage, by reducing losses due to lack of infrastructure and faulty technology.
Edge computing can be extremely useful in the energy industry, particularly for safety monitoring with oil and gas utilities. For example, pressure and humidity sensors must be carefully monitored, and cannot afford a lapse in connectivity. In case events like equipment overheating occurs, and goes unnoticed, the consequences could be catastrophic. The use of edge computing can prevent the occurrence of such incidents.
Another benefit is the ability to detect equipment malfunctions in real-time. With grid control, sensors could monitor energy produced by everything from electric vehicles to wind farms to help make decisions around reducing cost and make energy generation more efficient. Engineering conglomerate Bosch offers an edge-cloud platform that enables energy management at a residential level, while Tantalus Systems is developing smart grid systems that run on the edge to better automate load shifts for both commercial and residential customers.
With the growth of technology, retailers are becoming more inclined towards autonomous store development. Edge computing can play a major role here. For instance, Amazon opened its first Amazon Go store to the public. The store allows customers to swipe in with a QR code on their mobile app, at which point in-store cameras and sensors identify customers and register what they pick out to buy. These technologies are supported by edge computing, which makes monitoring easier and more scalable.
Additionally, edge computing can be useful in backroom functions, such as stocking up on popular items at times of peak demand and processing supply chain operations without a lag. Sensors placed on store shelves can help take inventory decisions based on demand and reduce time taken in manually stocking up items. Quicker data processing can help ensure that time, and money, is not lost as a result of sending data to the cloud.
While a centralized cloud or data center has traditionally been the most popular option for data management, processing, and storage, both have problems associated with it. Edge computing can provide a better alternative and is extremely important for enabling faster connectivity and enhanced network performance. It brings cloud services closer to the edge devices, while lowering latency and providing new applications and services to consumers