

This article explains the possibilities and benefits of using a blockchain based voting system for conducting secure and efficient election poll. Feel free to jump forward to the section that’s interesting for you.
A democracy is about transparency and fairness and any elections conducted within such a paradigm should reflect those principles. As the US Presidential Elections are drawing closer amidst the corona virus pandemic, a burning question has come to light — How can the elections be conducted when everyone is stuck at home, following the social distancing requirements?
It is expected that most of the American voters who would otherwise vote in person won’t come near the polling stations for fear of contracting or spreading the disease, which has infected more than 5 million and killed at least 170,000 people in the U.S.
In New Zealand, the Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern has decided to postpone the election by four weeks. The election that was originally scheduled for September 19 will now be conducted on October 17 due to a fresh wave of corona virus cases that broke out in Auckland.
Conducting elections would only boost the spreading of the pandemic. In this scenario, the state leaders have a few options that they can consider;
The mail-in voting option has gained the most attention in America. However, President Trump has claimed that this will make the election rigged. Moreover, many Americans are skeptical about casting their ballots via mail.
Following these reservations, the United States Postal Service (USPS) has filed a patent for a mail-in voting system that utilizes blockchain technology. According to them, a blockchain voting system will allow the tracking of the various types of necessary data in a way that is secure and allows others to easily confirm that data has not been altered.
Reach out to us today and get started!
In one suggested implementation, the voter would receive a paper ballot on which would be printed an individualized, computer-readable code. The voter could then scan the code with a mobile device, verify his or her identification, and then cast the ballot digitally. This system would separate the voter ID from the actual vote to maintain anonymity, with the votes stored on the blockchain.
But with so many arguments against online voting, can it really be superior to traditional voting systems?
Using the traditional voting systems during a pandemic could lead to more wide spread of the pandemic as voters are requested to cast votes from a voting booth, which are mostly crowded. With the exception of Estonia, that successfully implemented online voting in 2007, most nations still stick to the traditional mode of voting, i.e., paper ballots. It requires the citizens to be physically present at a location to cast their vote which may not make much sense considering how connected we are today. People shy away from digitizing the process because of security risks associated with putting everything online. However, there are many problems with the traditional mode of voting as well.
For example, the Turkish general election of 2015 was fraught with controversies and allegations of electoral fraud with Recep Tayyip Erdoğan and his Justice and Development Party (AKP) smack in the middle of it. The AKP allegedly used state resources like state funds, media, and vehicles for the campaign. The Supreme Electoral Council of Turkey also came under investigation for printing an excess of over 20 million ballot papers for a population of 50 million raising questions about how the surplus papers would be used.
This isn’t an isolated incident. Election fraud is a reality for many countries albeit to varying degrees. NGOs and IGOs are sometimes appointed to monitor elections. But they aren’t foolproof either. The monitors aren’t usually familiar with the lay of the land and they don’t collaborate with the locals to remain neutral which hampers their ability to effectively evaluate the votes. Also, in the case of IGOs, which are made of a group of countries, the monitors at times have to verify or risk destabilizing that region. Adding to that, since IGOs are made up of multiple countries, it’s always a possibility that the monitoring would be unwittingly influenced to serve those nations’ interests.
With so many issues surrounding the traditional mode of voting, it is safe to say that we need a safer option that could promote the transparency of the process.
Can we rely on blockchain technology for voting systems?
Simply put, Blockchain is a digital ledger. This technology is highly secure while affording an unparalleled level of transparency among authorized users. This is because all transactions are recorded on a “chain” maintained across millions of nodes on a network. It is cryptographically secure; you cannot edit or remove a single detail without the other parties verifying it. This makes it essentially immutable. Let’s see how we can integrate these features of blockchain into the voting system. If you’d like to learn more about the technology, check out this article explaining what is blockchain technology?
Reach out to us today and get started!
Voter Registration
The Estonian government, when they introduced online voting, assigned a national ID card with encrypted files that identified the owner. A blockchain enabled identity management system could record this information in an immutable ledger. Relevant authorities could be given access to this blockchain and the citizen’s information can be verified by government miner through local government administration offices in the district, government utility services like water and electricity. Once the individual’s information is verified to be accurate, they can be assigned a vote. This essentially eliminates fake voter data which is the main cause for allegations like dead people voting. This was something that came up during the Turkish elections.
Secure Online Voting
While a majority of the voting population shows up at polling stations to cast their votes, there are still a number of people who don’t show up at all. This indifference results in lost votes and lack of participation in the democratic process of the country. It’s usually because of the inconvenience; people would rather be in the comfort of their homes rather than out in a long queue, waiting for their turn to vote. If the voting can be done by phone or computer, then more people would join in the democratic process. We could use blockchain voting systems to secure online voting. Such an application wouldn’t have to worry about hackers because the processing power required to affect every single node on the blockchain is monumental.
Blockchain offers a number of options with which the actual voting can be made more secure.
Tokens as votes: In this case, each token would be a vote for a citizen. They can cast their votes from an electronic device linked to the blockchain and by virtue of being on a blockchain, no one would question the final count as every transaction is time-stamped and in case changes are made, a trail of the same would be present. Demanding recounts is something that many losing candidates resort to and it is a very costly process. By putting the votes as tokens on a Blockchain, we can discourage such demands.
Voting through smart contracts: In this case, the citizen can be assigned a smart contract vote which is valid for one execution on the election day. While the vote will be valid and secure, it won’t be anonymous. What can be done in such a case is by linking the public key of the voter to an alias that only the voter can access.
A number of approaches can be taken in order to successfully use blockchain technology for electronic voting. On hearing the term ‘blockchain voting system’, it is natural to wonder how such a system can be implemented. We have outlined a potential solution to this problem below. There are a few major points that are associated with the functioning of such a blockchain voting system.
The blockchain-based e-voting scheme is public, distributed, and decentralized. It can record votes from voters across many mobile devices and computers. It should allow the voters to audit and verify the votes in an inexpensive manner. The database of votes should be managed autonomously using a distributed server of timestamp on a peer-to-peer network.
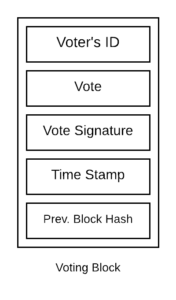
The voting blockchain is represented as a growing series of voting blocks chained to each other in a sequential manner. Each block contains voter’s ID, vote, voter’s signature, timestamp, and hash of the previous block. Public key infrastructure is a set of procedures that manage public-key encryption. Vote database changes according to the statistics of votes that are updated by the voting office and miners are responsible to deal with accepted votes and adding them to the public voting blockchain.
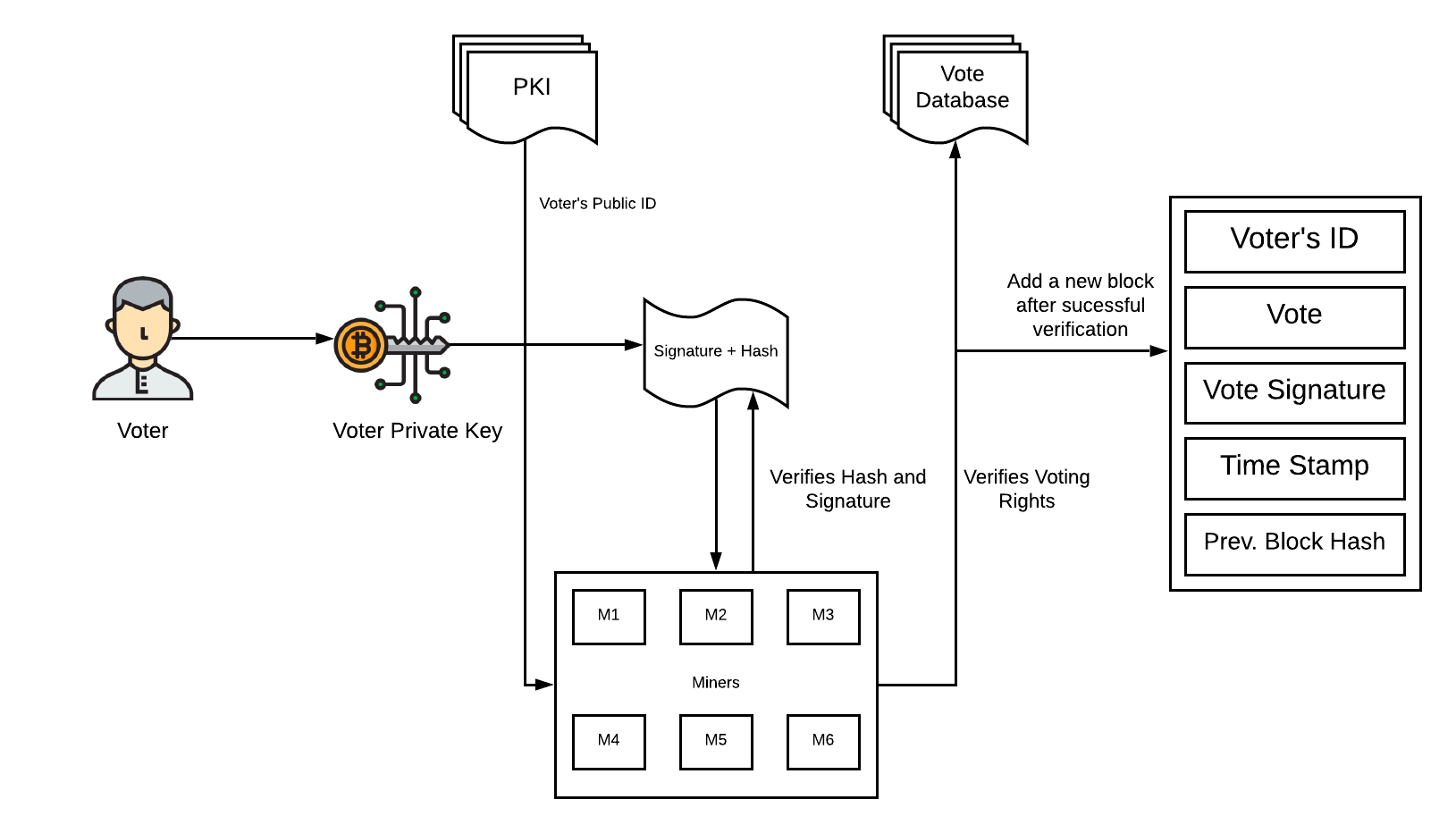
The voter’s voting interface creates a hash value of the voter ID, vote and timestamp. The program then uses the voter’s unique private key to generate a signature of the hash value. This signature and hash value is send to the miner block.
Miners are elected in random from the miner block and a miner obtains the public key of the voter from the PKI using the voter’s ID. Using the public key, a miner creates a new hash based on the data available from PKI and compares it with the hash sent by the voter. If both hashes match, the signature is verified successfully. Otherwise the signature is discarded.
The miner then sends queries and verifies that voter has the right to vote and after verification, the miner generates a new block with the previous block’s hash value and the information of vote and adds it to the blockchain.
Each vote is stored as a transaction on the blockchain and each voter receives the transaction ID for their vote for verifying purposes. Each vote is appended onto the blockchain by its corresponding ballot smart contract. The network is appended only if all corresponding district nodes agree on the verification of the vote data. When a voter casts his vote, the weight of their wallet is decreased by 1, therefore not enabling them to vote more than once per election.
Evidently, there are several advantages that can be experienced upon the implementation of blockchain voting systems. Some of the major benefits are:
Reach out to us today and get started!
Since the votes are recorded on an immutable ledger, blockchain voting systems can make the elections extremely transparent. Anyone can verify that votes have been recorded. Additionally, they are indisputable and probably unique. It is also very difficult to shut the election down or tamper with it, because the blockchain’s ledger is distributed across thousands of computers worldwide.
This is why many countries are finally becoming amenable to the idea of blockchain voting systems. The small West African nation of Sierra Leone was the world’s first country to have blockchain-powered elections. The reason behind using blockchain voting systems was to improve transparency and reduce suspicion of corruption.
For the past two years, the Thai Democrat Party’s primary election used an e-voting system based on privacy coin Zcoin, while the US state of West Virginia held a small-scale pilot using Voatz in 2018. In South Korea, the city of Seoul has launched a blockchain petition system that verifies the identity of people on the network to prevent duplicate votes. The coronavirus lockdown has encouraged the Arizona State Republican Party convention to use a blockchain voting system called Voatz as well.
The election process is the cornerstone of any democracy. It needs to be secure and transparent, so that the nation can elect competent leaders. The threat of the pandemic coupled with the increasing corruption faced in traditional modes of voting has emphasized on the need for blockchain solutions in the voting process.
If you’d like to discuss more about this topic, drop us a message.