

EOS blockchain is one of the many blockchain development platforms you or your company can choose for building its next dApp. Like any other platform, EOS has its pros and cons, making it the best fit for some business applications and not the recommended candidate for many other use cases.
In this article, we’ll learn about the EOS platform, how it works, and ponder on the use cases EOS platform can serve the best. I hope you’d get a clear picture of whether or not to use EOS for developing your blockchain project. Before jumping into the details, let’s brush up on the basics. In read forward, we’ll discuss;
Let’s get the terminologies right! EOS is a cryptocurrency and EOS.IO is a blockchain protocol based on the cryptocurrency EOS. EOS smart contract platform claims to eliminate transaction fees and also conduct millions of transactions per second.
EOS’s primary goal was to facilitate a simple interface for blockchain development without compromising security and management efficiency. With its ability to process millions of transactions per second, EOS is now gaining blockchain investors’ trust. Ever since the initial coin offering came into place in July 2017, EOS became very popular. Eliminating gas fees for processing transactions was the most attractive feature put forward by the EOS platform.
Like I said before, there are a few factors that make EOS a good fit for many business blockchain applications. The key highlights are in the easiness in the blockchain development, in which EOS offers a fast, flexible, and forward-driven interface for developers.
EOS blockchain offers industry-leading TPS ( transactions per second) rates. Which makes it the best candidate for building mission-critical blockchain applications that’d require millions of transactions to be processed in a second. It also offers high performance in the sub-second block time latency rate. The requirement for blockchain transactions to concise all nodes of a network at a given point for seamless pass-through of data makes transactions time-consuming and slow. However, EOS incorporated the distributed proof-of-stake mechanism (discussed later in this blog) to make the process rapid as well as accurate.
EOS platform offers a great deal for convenience in many aspects of blockchain development. You can use EOS to deploy public, private, permissioned or permissionless blockchain infrastructures. You can also develop custom programmable governance and business logic through executable EOS smart contracts. Moreover, it makes it easier for programmers with a simple interface for EOS development for building custom dApps.
EOS can process and measure millions of transactions per second. The advanced DPOS technology amalgamation made EOS’s framework is efficient enough to calculate a million transactions per second. The technology uses distributed proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. Also, the continuous requirement of a fast dApp platform allowing millions of simultaneously active users to act seamlessly makes EOS a preferred tool over others. It propounds no performance issues with a massive user base.
The dApps extended on the EOS blockchain are upgradeable. Isn’t it awesome?
The developers working on EOS can change, upgrade, and can also improvise the code. The incorporated feature for fixing or changing an application and functionality has increased the flexibility of this platform. To make this easier, the EOSIO experts also provide training and certification programs to get hands-on EOS upgradability skills for complete comprehension.
The developer-friendly side of EOS has established it as preferable blockchain software to expand products, features, and tools. After all, it eliminates the constraint of “only for experts” and is pretty friendly with blockchain novices.
The EOS operationality includes the division of program directions to multiple processors, thereby reducing the load on the program. The sensible contracts and functionality can be aided by two key elements:
In horizontal measurability, to improve the transaction speed, multiple systems and computers are added to the resource pool whereas, in vertical measurability, transaction speed is increased by boosting the processing power.
This removes the constraint on the availability of all parties in real-time and thereby eases communication and fuels time management assets.
With complete web security verification standards, the end-to-end encryption makes EOS a stable and efficient way of data integrity. The platform is completely safe and secure and is developed with essential safety norms and verification standards. Also, the blockchain platform is fairly equipped with trouble-shooting or malfunctioning savage mechanisms to elevate security levels.
For particularly the development of dApps, EOS is furnished with appropriate algorithms to make it robust among all blockchain platforms available. The complete functionality of EOS is accounted for by its DPOS mechanism, delegated proof-of-stake. Generally, other blockchain platforms operate on a proof-of-work mechanism that is relatively less secure, slow, and is error-prone. To completely understand the working of EOS, we must dig deeper into DPOS.
The process flows in the following steps:
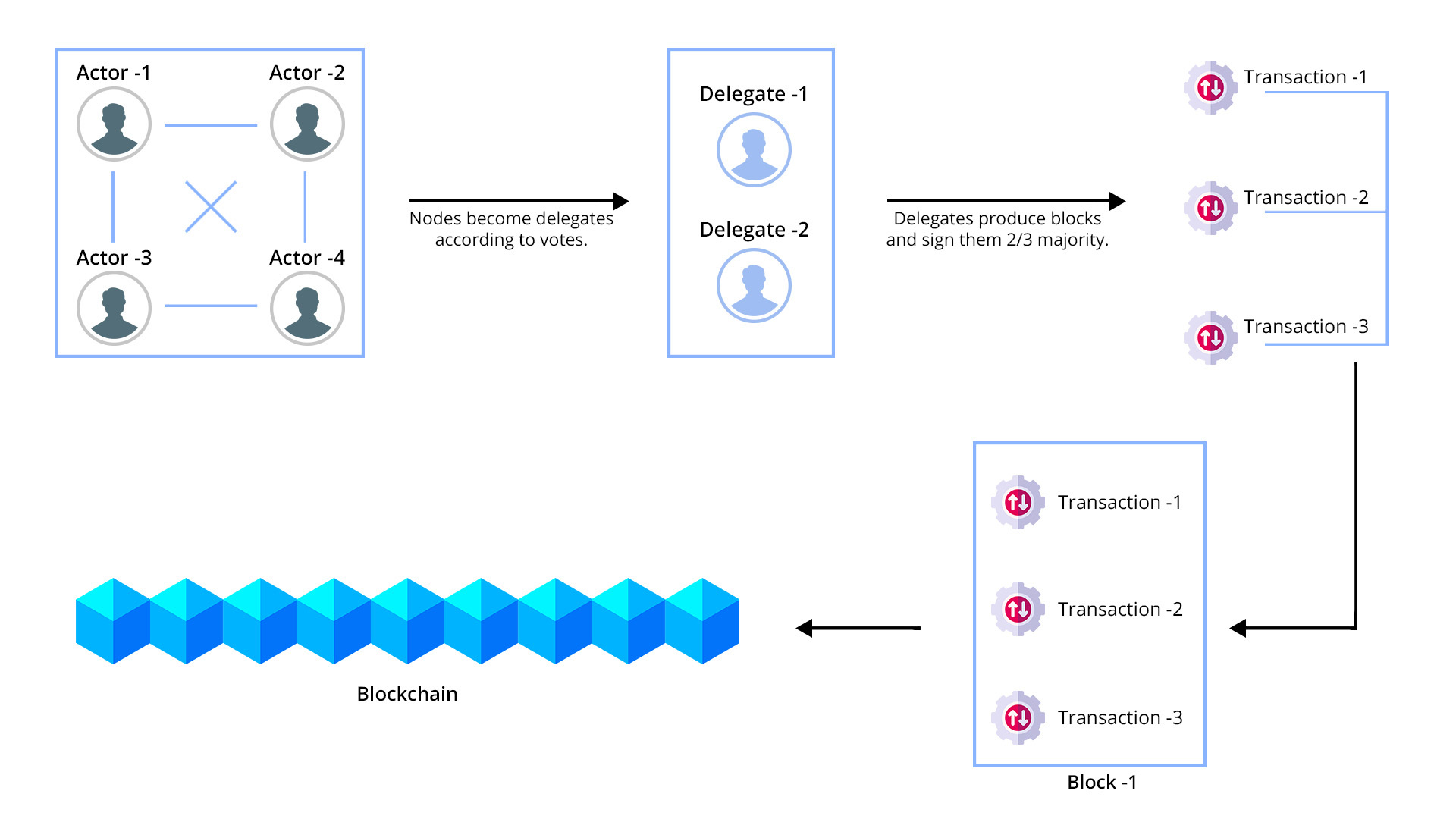
The major advantage of a continuous voting system is that anyone can participate in the election process to get blockchain rewards. This proof-of-stake, a.k.a DPOS integrated election system, enables networks of computers to get decentralized. This works according to the number of tokens each validator or participant owns. More tokens establish a greater role in resolving the EOS network. This approach is more rectified, preferred, and faster than the “proof-of-work” consensus system.
DPOS or delegated proof-of-stake is a consensus system to channelize cryptocurrency transactions seamlessly. With extra security and speed, the DPOS doesn’t experience a halt as it operates on the co-operation of producers instead of presenting competition for the blocks. In a condition of halt or malfunctioning, it automatically prefers the longest chain.
DPOS, is based on the voting and election process to protect blockchain. The decentralized framework makes it feasible for users and even for businesses.
It is more efficient, fast and cheap. To make it perfect for a decentralized system, the extra step of validation is added that makes it more reliable and usable.
This consensus protocol used in the EOS, DPOS, ensures the integrity and security integrity of the financial network running on it.
Reach out to us today, to discuss your projectNeed help with EOS blockchain development?
EOS.IO blockchain has its cryptocurrency known as EOS. Several reasons made EOS a preferred software over its competitor. Apart from the major perks discussed earlier in this blog, the massive advantage is free transactions.
For example, Ethereum charges its users a transaction fee called GAS, and this generally increases as more people join the network. This feature set a drawback for Ethereum to emerge globally and therefore established a need for another competent blockchain platform.
Initially, Ethereum used a renting mechanism where people were advised to rent Ethereum’s virtual machine to use the network after paying a transaction fee. However, EOS doesn’t operate on a payment mode.
Instead of transaction fees and renting virtual machines, EOS coin holders own a network. For instance, If you hold 3% coin stakes of EOS, you technically own 3% of network power to process the transaction. Thereby making transactions free and exchanging them for coin stake ownership. One can hold, receive or release funds among digital wallets in the form of EOS, just like any other cryptocurrency.
Another win-win situation!
How can blockchain benefit your business? What are the different business use cases of blockchain technology? If you’re having these questions in mind, have a look at the video below.
As we discussed earlier, one of the most important applications of EOS blockchain is in the full-fledged DApps or decentralized application development that needs very large transactional capacity. Since this blockchain assures user authentication at various levels, anyone can build a dApp, run it on the platform, and authorize various development authority levels while sharing data between users.
The Ubuntu Energy Ledger is a good example of a decentralized application developed by the EOS blockchain. This application is owned by a community aiming to provide cost-effective renewable energy to African countries. They are planning to power 4 billion households by 2030, With the aid of microloans and investors.
EOS can also be used as an investment tool in a crypto space or even a cryptocurrency. Even though the EOS token is not mined, the proof-of-stake system will provide the blockchain’s mining power. And as we saw earlier, there is no transaction fee associated with it, making it a fan favorite among developers. It is currently ranked 18th on the list of top crypto assets.
For example, DACTROIT is a decentralized platform backed by EOS, which is basically an experimental initiative to promote alternative ways of sharing spaces, resources, and relationships. Here communities are allowed to own and operate a parallel currency.
With a long array of promising features, EOS blockchain has now become one of the most assured blockchain platforms in the crypto world. Especially to build a well-managed, secure, user and business-friendly interface for dApps development. Unlike other blockchain development platforms, EOS offers zero transaction fees, thanks to its unique structuring.
Also, EOS comes with a lot of business applications, which are being successfully implemented all around the globe. Its consensus mechanism delegated proof-of-stake or DPOS ensures the integrity and security integrity of the financial network running on its platform, which makes them one of the top choices of developers.
As a promising blockchain platform, we can expect the EOS to continue to expand over the coming years, offering dApps that are much safer, faster, and affordable than traditional blockchain applications.
By reaching out to us todayHire our blockchain developers?