

Dagger2 is written in Java and Koin in Kotlin, and using both libraries in a Kotlin project should not be a challenge. However, implementing Koin in Java could be a little tricky. One notable information worth mentioning is that while Dagger2 is a fully acknowledged DI project, where as Koin is only described as a Service Locator.
In Android programming, handling dependency is a big concern. For the past few years, we are mainly using Dagger2 for the dependency injection. There is no doubt Dagger2 is one of the best available dependency injection framework now available. Now you can ask, as of now we have Dagger2 then why do we need to think about another framework?
Getting started with Julia language- Part 2, REPL and Packages
Simply speaking… Dagger 2 is a dependency injection framework. It is based on the Java Specification Request (JSR) 330. It uses code generation and is based on annotations.
Dagger 2 uses the following annotations:
@Module and @Provides: define classes and methods which provide dependencies.@Inject: request dependencies. Can be used on a constructor, a field, or a method.@Component: enable selected modules and used for performing dependency injectionDagger 2 uses generated code to access the fields and not reflection. Therefore it is not allowed to use private fields for field injection.
Koin is a practically sensible and realistically lightweight dependency injection framework for Kotlin developers. Written in pure Kotlin using functional resolution only: no proxy, no code generation, no reflection!
Koin is a Domain Specific Language, a lightweight container and a pragmatic API.
From the above statements, it is very clear both have the same functional requirements but the differences are very few isn’t it? To make it simple let’s go through simple real statistics which I observe.
Choose from our pool of experienced developers
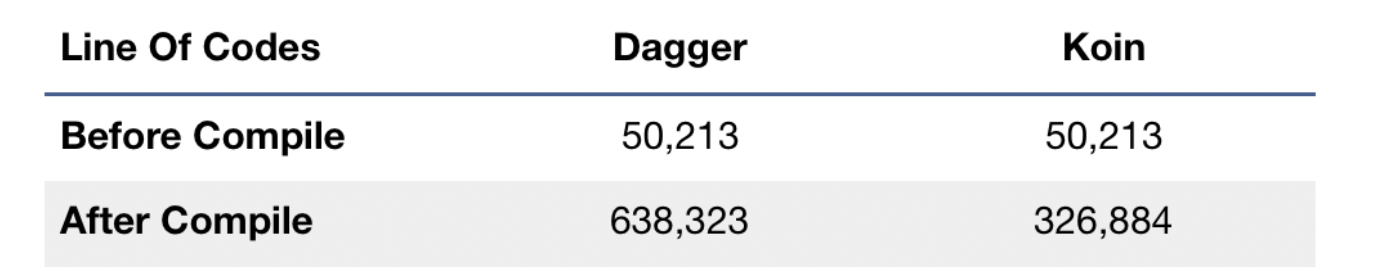

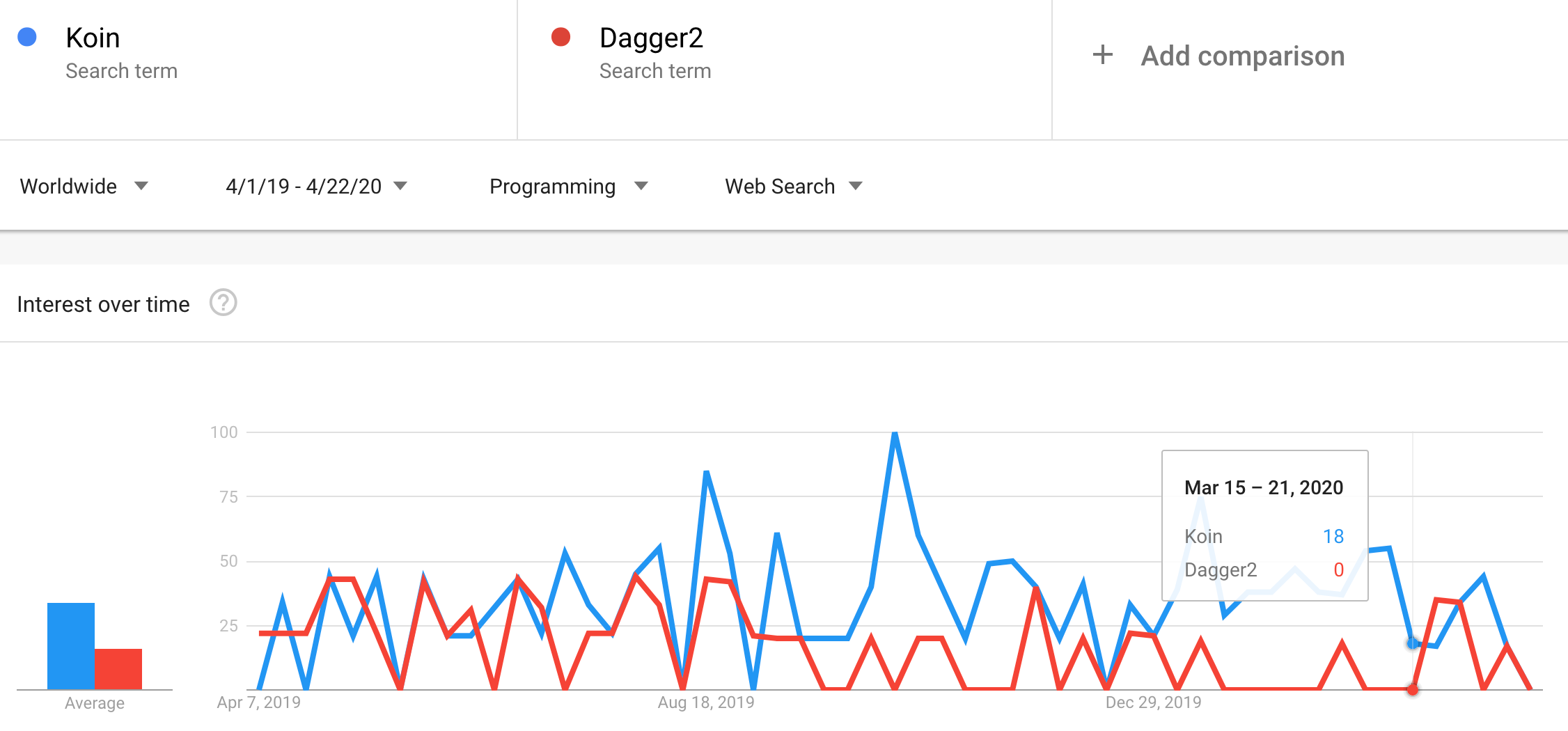
From the above statistical observations, it is very clear koin gains more points over Dagger2. Also from a developer perspective, I really do prefer koin more than Dagger2. Because implementing Dagger2 is a painstaking effort and moreover the debugging of Dagger2 (Ohh…) you will struggle. It may be a small issue, but because of the generated code, it will be a nightmare to fix it. And also learning Dagger2 is hard, so if someone joins your project or team he/she has to spend a lot of time on learning Dagger2.
Okay now, let’s answer why Koin?
Just add this line to your Gradle.
// Stable Koin Version
koin_version = "2.1.5"repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
// Koin for Android
compile "org.koin:koin-android:$koin_version"
// or Koin for Lifecycle scoping
compile "org.koin:koin-android-scope:$koin_version"
// or Koin for Android Architecture ViewModel
compile "org.koin:koin-android-viewmodel:$koin_version"
}
And create your module file, Go On… Happy Coding!