

Imagining a world without the internet is difficult. It has become an essential part of the modern world. It would be impossible to picture our lives without it, especially in light of a worldwide epidemic that has compelled most of us to turn on the internet for our occupational, communicative, educational, financial, and recreational needs—arguably with greater urgency than ever before. As our reliance increased in the last 30 years, the internet has undergone some seismic shifts. And the next phase of its development is now clearly visible, and that’s Web 3.0.
Here, we’ll help you gain better insights into the below topics:
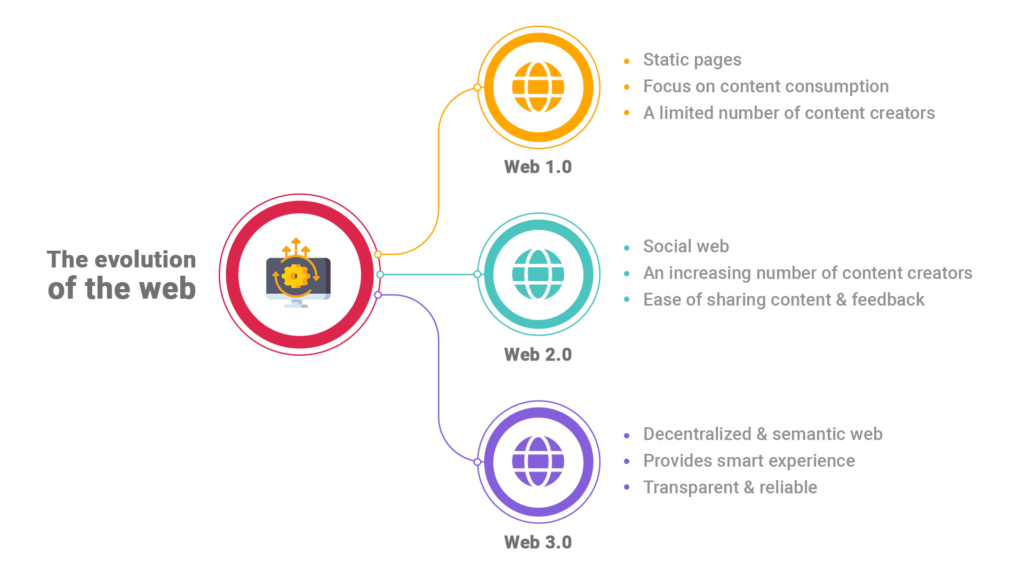
Well, scraping past timelines would help us understand the significance of these enhanced updates. Web 1.0 marked the beginning of the internet with read-only websites. Even though it was only accessible to limited users, it was a significant advance, allowing people across the globe to view published content. Users could read and explore such web pages but couldn’t engage with them much further. And the search engines were not that advanced during this iteration (at least this iteration saved people from worrying about SEO and page rankings).
Web 2.0 paved the way for digital content creators, enabling the privilege of user engagement and participation. Users could create a distinct digital identity for business and personas, creating huge prospects for business, notably e-commerce, as new internet enterprises could promote their products and services to a global audience of prospective online consumers at a low cost. The introduction of cloud computing revolutionized the management of data and infrastructure. Cloud providers consolidated the need for mass hardware by bringing data and connecting it through global data centers. Scaling a business became much more cost-effective as enterprises rent storage, computing power, and management tools.
It also meant that anybody with access to the internet could publish content to a global audience, giving rise to the internationally widespread practice of blogging and fueling user-published sites such as Wikipedia, which became enormously successful. And, of course, one cannot overlook Web 2.0’s role in supporting the emergence of social media, with Myspace as first and then, more explosively, Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube as the user-generated content revolution escalated to the next level.
Related article on Driving business innovations in the post-digital era with DARQ
Web 3.0, in other words, known as the decentralized web, represents the latest generation of internet applications and services enabled by distributed ledger technology. It is primarily concerned with linking data in a decentralized manner rather than storing it in centralized repositories, with technology capable of interpreting information as intelligently as people. As a result, people and machines will be able to link more efficiently with data, emphasizing that artificial intelligence (AI) will play a critical role in making this version of the internet more intelligent and powerful in terms of information processing.
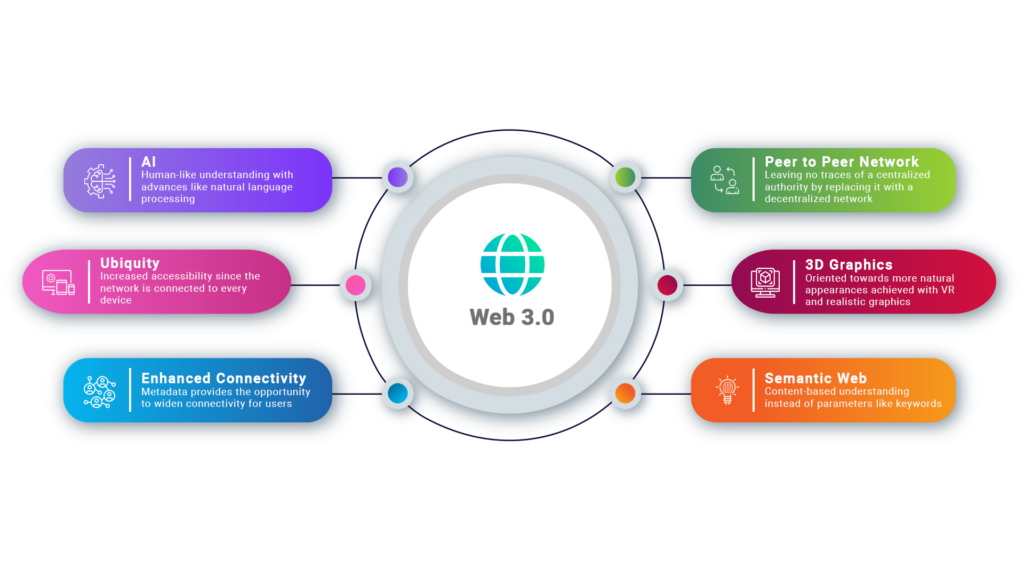
In the end, this will allow machines to more precisely comprehend the meaning underlying the data—or its semantics—to provide substantially smarter user experiences.
Related article on How to implement Artificial Intelligence in your business and measure its impact
Web 3.0 was developed by considering the shortcomings of Web1.0 and Web 2.0. Its decentralized architecture aims to solve the challenges arising from user trust, privacy, and transparency. With seamless interaction between humans and machines, the fluidity it offers can mean a lot for businesses in the current era. Some of them are:
Related article on What are Web3 DAOs and their benefits?
Wolfram Alpha and Apple’s Siri are examples of Web 3.0 applications that can summarize enormous volumes of information into knowledge and relevant results for users.
Wolfram
When comparing the search results of Wolfram with other search engines, you can see the major difference in the results it covers for each user. It provides more viable information in terms of analytical and graphical representation. It feels like results are personally tailored to your demand.
Siri
On the other hand, Siri employs speech recognition and artificial intelligence algorithms to provide results and conduct tasks. Traditional technologies (Web 1.0 and 2.0) do search matching on the text “word for word like” concerning what is published on the network.
In other words, it frequently introduces information bias based on what is most plentiful, not presenting what is most relevant to the user.
Related article on How to implement Artificial Intelligence in human resource management
The new internet will offer a much more personalized surfing experience, smarter search engine services, and decentralized benefits that’ll contribute to the formation of an egalitarian web. That will happen when each user becomes sovereign over their data, and, as a result, many innovations will be implemented once it is in place.
When Web 3.0 hits — difficult as it is to imagine, smart devices have already impacted our behavioral patterns — the internet will become exponentially more embedded in our daily lives. Today’s offline machines, such as home appliances and transport, will become part of the IoT economy. It’ll interact with its autonomous servers and decentralized applications (dApps), advancing to new digital realms like blockchain and digital assets to power a mountain of new tech “miracles” for the 21st century.
Reach out to us today