

A study by Gartner found that automation can save upto 25,000 hours of labor. Looking at industries that could use Robotic Process Automation (RPA), FMCG, or Fast-Moving Consumer Goods definitely stands out. RPA in FMCG is especially because such goods include everyday consumer products with very little shelf life and must constantly be in the supply chain loop. This means many mundane continuous processes must be done in the same pattern daily, and automating them with advanced robotics can save time, energy, and money and even prevent errors.
In this article, we will look at how RPA is included in the processes in the FMCG industry.
Recently, because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for convenience has shifted gears, and new-age technologies are coming up with innovative solutions. Recent trends in the FMCG industry include blockchain, e-commerce, augmented and virtual reality, and the currently trending RPA. Let’s look at some of the trends below.
FMCG e-commerce
Companies have started expanding their digital footprint by setting up online shops. Due to that, e-commerce sales are increasing exponentially. This has also caused a shift from physical in-store retail shopping to online. To boost branding and reputation online, recent trends in FMCG includes avid use of social media and platforms such as website and apps.
AR and VR
AR and VR technology are booming nowadays. Especially because of their usage in metaverse and web 3. Meanwhile, virtual and augmented reality elements in the FMCG industry are being used to improve customer experience. This is being seen in the form of virtual shopping, virtual tours, and more.
Blockchain
FMCGs are using blockchains with smart contracts enabled to have a competitive edge. The traceability feature offered by blockchains lets consumers and manufacturers track the source of products. Additionally, Information about products, such as nutrient content, usability, and other details, can be stored on the blockchain to be viewed by customers. We now see retailers using crypto reward programs as incentives for increasing customer engagement.
3D Printing
Sectors from personal care to food products have opted to go by the sustainability route. 3D printing allows FMCG manufacturers to design more eco-friendly products while reducing plastic usage. 3D printing allows manufacturers to test the form and fit of products and, in some cases, even the designs in real-world-based simulations.
RPA Automation
One of the upcoming tech solutions includes Robotic Process Optimization (RPA). Even though FMCG requires intense manpower, there are repetitive tasks that, when automated. Businesses are using RPA to save a ton of time and energy.
Let’s look more into Robotic process automation.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA), also known as software robotics, is a technology developed to perform specific tasks that are usually done by humans. This can include extracting data, moving files, filling forms, and more. People often compare RPA and AI, but to define RPA exclusively, RPA technology automates businesses that have rule-based and repetitive processes. Robots are generally designated to middle and back-office processing centers. It is aimed at increasing productivity, efficiency, accuracy, and speed much higher than manual labor performed by humans. Since robots can easily perform such tasks, we can employ human skills in higher-level activities, thereby becoming more efficient.
According to Gartner, global spending on RPA technology is expected to reach $2.4 billion by 2022. RPA prevents human error and reduces labor costs considerably. Software robots used in RPA can open and read email attachments, fill e-forms, record data, and more. For instance, a report by Deloitte mentioned a bank that deployed 85 software bots that ran 13 processes and handled 1.5 million requests in a year. The bank was able to get the capacity of 230 full-time employees at 30% of the usual cost.
Contact us for a no-obligation consultation
RPA technology has been deployed widely in the retail industry. An example of a use case would be: Shop Direct, a retailer in the UK, used RPA to automatically identify areas affected by floods to remove late payment charges for them. Likewise, RPA has been used in workflow management, customer support management, Accounting Finance, and more. We will talk about the use cases in detail in the next section.
As we deduced earlier, FMCG has a lot of sectors that can use automation instead of wasting precious human resources. Let’s look at where exactly RPA can come into use.
An RPA action bot can be implemented onto existing websites without significant adjustments and as a shopping advisor. These action bots can automatically fill out forms and collect feedback from potential customers. The upselling capabilities of the action bots enable them to give personalized suggestions and recommendations to customers.
Machine learning components such as the customer’s previous purchase records stored in RPA chatbots can be used to provide the next product recommendation. The RPA action bot and media such as WhatsApp provide intelligent shopping solutions. Integrating a WhatsApp bot with an RPA action bot can bring in features like online shopping, bill payments, query management, virtual home tour, etc.
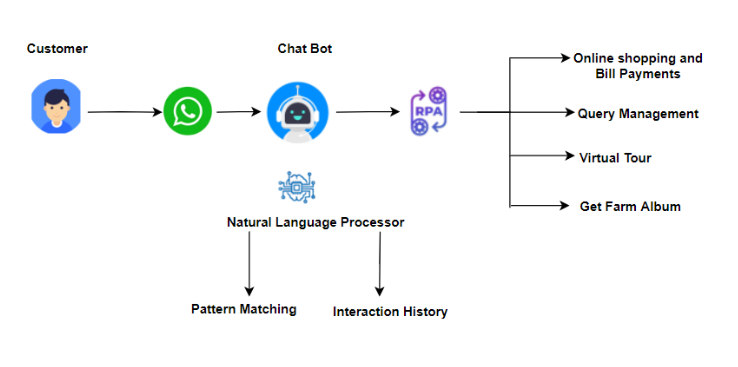
With the world going fully digital efficient, less interactive business solutions as static websites could result in potential business loss. According to a survey, 97% of consumers go online before purchasing to research products and services locally. Data by the WAV group also suggests that listings with virtual tours get clicked on 40% more than listings without them.
Hybrid RPA and AI can produce solutions to make business platforms more interactive.
This is where an engaging, smart website plays an important role. Virtual tours with automated elements can be conducted where people log in and go around farms (beneficial for shops that sell food products), shop buildings, other branches, and so on. Embedding an option for virtual tours gives a more immersive customer experience and can attract website traffic and increase customer retention. Users will be directed to a 360-degree virtual overview and can interact with 2D articles and gain information while exploring or even doing virtual shopping, throughwhich, customer interaction is also said to increase manifold.
Customer behavior and preferences are changing fast, and not keeping up with the trend would result in the potential loss of promising consumers. According to a McKinsey & Co. report, 75 percent of consumers in the United States tried a new store, brand, or different way of shopping during the pandemic.
The data proves that to understand customer trends and behavior, the best solution is to analyze and understand the emotions or sentiments behind every customer’s feedback and needs. We can do this with the help of RPA by combining it with sentimental analysis. The company will have a holistic, intelligent automation strategy to solve its business problems.
Get in touch with us today
For instance, RPA extracts textual data from various sources like the company’s website, social media, surveys, emails, support tickets, and other written feedback. The extracted data serve as the input for sentiment analysis. Each feedback item will be mined to determine the tone using Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques/ machine learning techniques. The output of sentiment analysis is the automatic categorization of each feedback as “positive,” “negative,” or “neutral,” and/or the feedback is given a quantitative score. The score can later be used to understand the customer’s shopping preferences.
The back office maintenance and management of retail file reports is a cumbersome and tiring task. The managers must validate the cash registers against the transactions before submitting them to the central administrative office, which requires much time and effort. Similarly, for taxation purposes, the retailer usually struggles through the suppliers’ websites to download and use the invoices to reconcile, which is very time-consuming and error-prone. Such activities prevent the employee from being productive and drastically impact customer-centric activities.
For example, an RPA-based solution would mean that bots can read the input as requested and gather the required information in seconds. They are designed to efficiently handle tedious and repetitive administrative and everyday data entry and documentation tasks. They can also automatically download the invoices from the vendor’s websites and store them centrally in the company’s cloud drive.
The bots validate and verify the data present on the documents with that in the company’s internal database. They also prepare internal and external financial reports for the management by integrating data from varied sources. Duplications in payment are checked across receipts, purchases, and sale orders, and concern accounts are notified.
Inventory management is quite challenging in the retail industry, requiring managers to analyze data from several sources, including third-party suppliers and business partners. About 63% of inventory data and stock information is always inaccurate or flawed. A GS1 US survey in 2014 revealed the same. A paper by Deloitte explains how disruptions in the overall supply chains regarding covid and how firms find it difficult to ascertain the demand, location, and pricing of their products. Manual handling of invoices is paper-intensive and requires many monthly working hours. It slows the entire process, resulting in hefty penalties, payment delays, and errors.
RPA software, combined with Machine Learning capabilities, can minutely analyze the data to customize the right strategy for the store-specific stock arrangement. ML-based backend extends the expertise to the company to analyze big data generated from several sources like the website and physical stores. The software can also track deadstock while limiting the risk of stockouts during peak demand times.
Bots can complement the back office work by forecasting demand, tracking inventory flow, and sending automated alerts to the concerned authorities in the prospective situation of a deadstock. Retailers can immediately discover stockouts and replenish them on time due to hassle-free and fast data transmission between multiple technologies, including outdated systems. RPA bots collect the information and compare it with the previous trends and when the stores typically face stockouts. They also scan, digitize, and check critical data from purchase orders to prepare invoices.
In the current scenario, although many companies use software like SAP and Oracle, many manual processes happen over this software. An article by IBM suggests that “the procure-to-pay cycle heavily relies on accurate data and the preparation of several documents. The partner onboarding process is also highly labor-intensive, with physical checking of the credit history, track/service record, etc.” Also, essential supply chain activities like demand/supply planning, purchase/sales order processing, shipment information recording, etc., are still very paper-hungry in most companies today.
Contact us for a consultation on RPA
As a solution, RPA as a Service is programmed to automate the supplier onboarding process end-to-end from research, invite, approval, to enrollment. Bots can send out the already prepared questionnaires to the suppliers and intelligently process the received data, further sending the insights to the concerned authorities. The RPA solution automatically checks the credit ratings of a new supplier/client for onboarding purposes, alongside third-party reference checking. Bots also copy data from supply chain management systems like Oracle and SAP Ariba into standardized order forms, thereby streamlining the process.
While the bots can also be equipped to submit orders through the online portal, they can also process invoices by ingesting the data into the company’s existing accounting software. The RPA solution can run multiple bots and scale up to prepare comprehensive reports to aid management demand and supply planning decisions.
Dairy farms are labor-intensive as they have to consistently track and look after the well-being of animals, resulting in huge amounts of money being invested in labor that otherwise can be saved. A study undertaken in Ireland revealed an estimated labor requirement of 41.3 h/cow per year for an average herd of 77.4 cows. According to a report by Michigan University, labor as a cost of production is usually the second greatest cost on the farm after fodder. Manual rearing of animals in the dairy sector is prone to errors, and there are instances when the laborers miss out on the milking timings, medical conditions, herd management, etc.
As a solution to these problems, AI-RPA IoT-based cattle monitoring system can help reduce the load of repetitive tasks slowing down the sector. Farming and RPA in agribusinesses has enormous potential and can be in charge of market and manufacturing operations.
Let’s look at how an RPA system can help monitor cattle’s health and activities.
The electronic tag is embedded with different sensors like temperature sensors, accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sound sensors to collect information from the cattle.
The data is sent to a wifi module through Bluetooth and a cloud ecosystem. A baseline is then set for the cow for its activities using the RPA-ML Algorithm, and if the cows deviate from the baseline, it’s a sign something is wrong. Users can thus keep track of the well-being of the cows and stay updated on their reports through a handheld smartphone app or a web-based portal.
When cows and other livestock are unwell, they produce substantially more methane, contributing further to climate change. According to research, sick livestock produces more methane when compared to healthy ones. With mostly CCTV cameras in dairy farming spaces, the systems are not smart enough to detect unusual grazing patterns and body language of the cattle due to sickness. The dairy companies cannot spot medical issues in the cattle proactively in any way. AI-based and automated technology can help detect anomalies in cow behavior, informing the farmers and preventing indirect effects such as carbon emissions.
The world is constantly driven by FMCG industries that serve our everyday purposes. The FMCG is also labor intensive and cannot risk errors as it constantly needs to keep moving, in the food supply chain especially. We are encountering technologies such as Robotic Process Automation that can perform tasks quicker and reduce human error. Robotic process automation has evolved from automated washing machines and dishwashers to do simple yet time-consuming tasks to bots that can monitor user sentiments and read emails. In an economy dominated by e-commerce, RPA continues to play a major role along with AI. The market size of RPA is expected to increase upto 23.9 billion by 2030 with a CAGR of 27.7%. We can confidently say that RPA is one of the technologies poised to become a necessity in the near future.
Contact us for a no-obligation consultation